Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Dubbing: The Key to High-Quality and Engaging Global Content
Updated: April 4, 2024
Artificial intelligence (AI)-based dubbing solutions are emerging as a way to make videos accessible globally. But can AI deliver the quality necessary?
Enter human-in-the-loop (HITL), a critical part of any successful AI dubbing workflow.
In this blog, we will explore common approaches to the dubbing process, what HITL means, its application in AI dubbing solutions, and the role it plays in supporting high-quality dubbing experiences for viewers.
The Dubbing Process and Common Approaches
Dubbing plays a key role in the globalization of content. It is an audio-based localization technique that allows viewers to enjoy media in their language of choice.
The dubbing process involves replacing the original audio track of a video with a translated version in a different language. There are a few different approaches that can be taken with dubbing:
Traditional Dubbing
The traditional dubbing process is most commonly used within the media and entertainment industry. Traditional dubbing requires creating a script, hiring voice talent, recording the dubbing track, post-production editing, and publishing. These factors can make for a lengthy, manual, and expensive dubbing process.
Traditional dubbing has been the standard for long-form, cinematic content as high-profile production studios often possess the budget, resources, and expertise to produce traditional dubs.
AI Dubbing
Automated
A purely automated AI dubbing process relies on artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to automatically generate dubbed audio tracks for video content. Completely automated dubbing solutions allow for greater affordability and flexibility than traditional dubbing. However, the use of AI without human intervention often yields low-quality dubs.
Human-In-The-Loop (HITL)
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) dubbing uses advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to automate critical dubbing steps, while also incorporating human oversight and expertise. This process ensures a high-quality output at a fraction of the cost.
HITL dubbing is a valuable choice for organizations with high localization standards that do not possess the budget or timelines for traditional dubbing.
What is Human-In-The-Loop (HITL)?
Before we analyze HITL dubbing in greater detail, let’s take a step back and learn exactly what human-in-the-loop means.
HITL has become a critical part of many AI-based accessibility solutions, helping to increase efficiencies while maintaining the high levels of quality and accuracy needed to support equitable digital experiences.
At 3Play Media, the foundation of our captioning and media accessibility solutions is rooted in HITL workflows and the ethical use of AI. For over 15 years, we have leveraged HITL to blend the best of human expertise and AI technology, creating accurate, high-quality media accessibility solutions, with efficiency and scale.
In general, HITL is used for AI technology in a variety of industries and has a wide range of applications, including:
- Marketing and website copywriting assistance
- Fraud detection solutions for financial institutions and IT sectors
- Flight simulations for pilot trainees
- Improvement of diagnoses and treatment of diseases in medical fields
- Autonomous vehicle development in the automotive industry
How Human-In-The-Loop (HITL) Works in Dubbing Solutions
Human-in-the-loop workflows have become more common in digital accessibility solutions, particularly with captioning. As AI speech recognition and language models have continued to evolve and advance, they’ve also become relevant to other accessibility solutions, such as dubbing and other localization services.
Several AI-based models are powering the development of scalable automated dubbing solutions:
ASR and Other Speech-Based Enhancements
Advancements in areas such as automatic speech recognition (ASR), speaker recognition models, speech timing detection, and machine translation models are driving greater accuracy rates in the areas of transcribed speech and translations, speech timing, and the identification of distinct speakers.
While traditional dubbing solutions require the time and work of skilled transcribers and translators to create a script for the spoken video content, AI leverages the aforementioned features to generate a source script. The script can then be fine-tuned through a HITL dubbing workflow to enhance quality.
According to our 2023 State of ASR Report, ASR accuracy rates have never been higher. This accounts for AI dubbing solutions’ ability to capture more accurate transcriptions that align with a source video’s timing and speaker changes. Still, our report maintains that human oversight and HITL workflows remain indispensable in producing high-quality outputs in AI-based accessibility solutions, including AI dubbing.
Synthetic Voice Options
Synthetic voice advancements are also propelling AI dubbing solutions forward through a variety of options like synthetic native voices, matching, and cloning. Similar to synthesized speech used in audio description solutions, synthetic voices can allow for greater user control, more precise language, and faster production times when incorporated into HITL workflows.
Traditional dubs utilize voice artists, who are contracted to record a dub and then move on. This can complicate production budgets and timelines when changes to a script must be implemented. The voice artist must either be contracted again, or the dub may even become delayed or need to be entirely re-recorded if the original voice artist is unavailable.
AI dubbing, on the other hand, supports last-minute adjustments and post-production changes inherent to the dubbing process through flexible synthetic voice options.
Each of these AI advancements helps to enable a holistic, high-quality automated dubbing solution. However, it’s important to note that each model also introduces a level of error throughout the process–technology is not 100% perfect, after all!
When an AI dubbing solution is purely automated and relies only on AI for each step, a significant degradation in a dub’s quality and accuracy is often observed. That’s why human-in-the-loop is vital to any AI dubbing solution.
HITL bridges the gap between technological efficiency and premium expertise, enabling human experts to provide real-time feedback and adjustments during the automated dubbing process to ensure a high-quality dubbing experience.
Why Human-In-The-Loop (HITL) Supports Cultural Sensitivity and Accuracy in Dubbing Workflows
A recent Preply study found that within the top five countries with the highest volume of foreign content viewers, four of the five prefer to view content with dubbing. And though viewer preferences vary between countries, data from Netflix shows that dubs’ popularity is on the rise–with the consumption of dubbed content rising 120% annually!
The increased popularity of dubbed video content presents a huge opportunity for organizations looking to extend their reach on a global scale. However, this opportunity comes with a big challenge:
- Organizations can choose a traditional premium dubbing solution, which will give a highly accurate dub, but includes a lengthy turnaround and hefty price tag.
- They can also choose a purely automated AI dubbing solution, which is scalable and budget-friendly, but poses brand risk concerns. Poorly executed AI dubbing can create distrust with target audiences in new global markets when quality, accuracy, and cultural nuances are not incorporated via HITL.
With such extreme options in dubbing solutions, it’s easy to see why many organizations might opt to only use subtitles. But human-in-the-loop is changing this in the AI dubbing space.
Human involvement in the AI dubbing process promotes the efficacy of the content, providing a more valuable experience for the end user. That said, adding any human to the process does not guarantee cultural sensitivity or translation accuracy. The human-in-the-loop portion of the dubbing workflow requires skilled translators and native speakers who can seamlessly navigate the spectrum of translation and transcreation.
Transcreation is important when dubbing content for diverse audiences across the globe. While verbatim automated translations may be accurate, they can end up becoming confusing and a little too literal, drawing greater attention to cultural gaps and barriers. Incorporating HITL into these automated workflows provides nuanced translations that support the intended meaning.
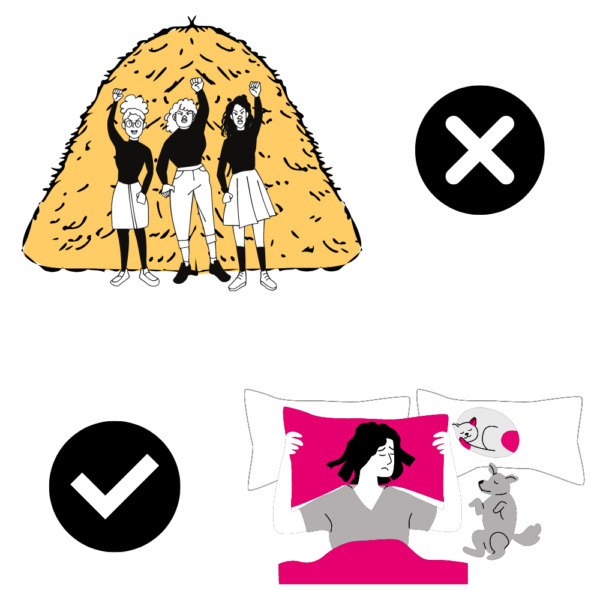
For example, a common English phrase like “hit the hay” is not usually intended to be literal–although a purely AI solution may translate it exactly as such in the target language.
In a HITL dubbing workflow, a translation expert would instead adjust the phrase to convey the actual meaning of “hit the hay” as going to sleep. For audiences in Spain, a translator may use a colloquial translation of “irme al sobre”. The same translation expert might change it again for Latin American Spanish (LAS) audiences as “tirarme en la cama,” and so on.
Using experienced translators through HITL can bridge these cultural barriers by making appropriate transcreative decisions to produce an authentic and immersive dubbing experience. Plus, with AI dubbing tools at their disposal, these experts can assess cultural accuracy, context, and linguistic nuances even faster than they could under traditional dubbing processes.
Advantages of Using Translation Experts for HITL Dubbing Workflows
- Improved linguistic accuracy
- Culturally appropriate translations
- Flexibility for real-time translation adjustments
- Ability to handle complex language nuances
What the Future Holds for Human-In-The-Loop AI Dubbing Solutions
As the demand for dubbed content grows, AI-based dubbing solutions will continue to emerge in the localization space. It will be critical for organizations to research vendors and solutions to ensure content is dubbed through a workflow that best serves their audience and globalization needs.
AI or automated dubbing solutions that utilize human-in-the-loop workflows are poised to become integral to many organizations’ global video content strategies due to the unique blend of advanced technology and the cultural expertise of translation professionals. And with ongoing advancements in machine learning (ML) and AI, these dubbing solutions will only continue to gain efficiencies and increase accuracies in the future.
Human-in-the-loop AI dubbing solutions enable organizations to incorporate dubbing into their content localization workflows at more attainable costs while preserving cultural accuracy and quality. Subtitles remain an important part of the localization process, but dubbing offers a unique opportunity to provide a listening approach that boosts engagement with your video content. And most importantly, providing a dubbing track on your video gives your audience the choice to engage with your content the way they prefer.
Are you ready to globalize your video content?
3Play Media’s revolutionary AI Dubbing service provides a high-quality dubbing experience at a fraction of the cost of traditional dubbing. Get started today: